diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram Ketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology calgary nursing guide physiology pathology treatment medical concept map ucalgary calgaryguide ca hhs sheet complications bacterial
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if left untreated. It occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. These ketones are produced when the body breaks down fat for energy in the absence of insulin, which is necessary for glucose uptake into cells. The pathophysiology of DKA is complex, but it can be simplified as a series of events that occur when there is insufficient insulin in the body. Insulin deficiency leads to increased glucose production in the liver, which in turn leads to increased glucose levels in the blood. When the body cannot use this glucose for energy, it begins to break down fat for energy instead, producing ketones in the process. The accumulation of ketones in the blood leads to a decrease in blood pH, which can cause a wide range of symptoms and ultimately lead to coma or even death. To better understand the pathophysiology of DKA, it is important to consider the role of insulin in the body. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood glucose levels. When insulin is deficient, glucose cannot enter cells and is therefore unavailable for use as energy. This leads to a state of starvation in the body, which triggers the release of hormones such as glucagon and cortisol that increase glucose production in the liver. At the same time, the body begins to break down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketones. In a healthy person, insulin acts as a check on this process by inhibiting the production of ketones. However, when insulin is deficient, this check is removed, and ketone production can proceed unchecked. The symptoms of DKA can vary widely depending on the severity of the condition. Early symptoms may include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and weakness. As the condition worsens, symptoms may progress to include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and confusion. In severe cases, DKA can lead to coma or even death. Treatment for DKA typically involves hospitalization and intravenous fluids to restore hydration and electrolyte balance. Insulin therapy is also initiated to lower blood glucose levels and halt the production of ketones. It is crucial that DKA be diagnosed and treated promptly to avoid severe complications. In conclusion, diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if left untreated. The pathophysiology of DKA is complex but can be simplified as a series of events that occur when there is insufficient insulin in the body. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for a successful outcome, and anyone with symptoms of DKA should seek medical attention immediately.
If you are looking for Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Images about Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube like Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Type 1 Diabetes: Love Hailey | Diabetic and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Type 1 Diabetes: Love Hailey | Diabetic. Here it is:
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis : Animation ~ MedchromeTube
 tube.medchrome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic diagram dka diabetes animation mechanism coma diagnostic tests diabetestalk walgreens a1c accuracy test glucose blood ph
tube.medchrome.comketoacidosis pathophysiology diabetic diagram dka diabetes animation mechanism coma diagnostic tests diabetestalk walgreens a1c accuracy test glucose blood ph
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Calgary Guide
 calgaryguide.ucalgary.caketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology calgary nursing guide physiology pathology treatment medical concept map ucalgary calgaryguide ca hhs sheet complications bacterial
calgaryguide.ucalgary.caketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology calgary nursing guide physiology pathology treatment medical concept map ucalgary calgaryguide ca hhs sheet complications bacterial
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Algorithm - Manual Of Medicine
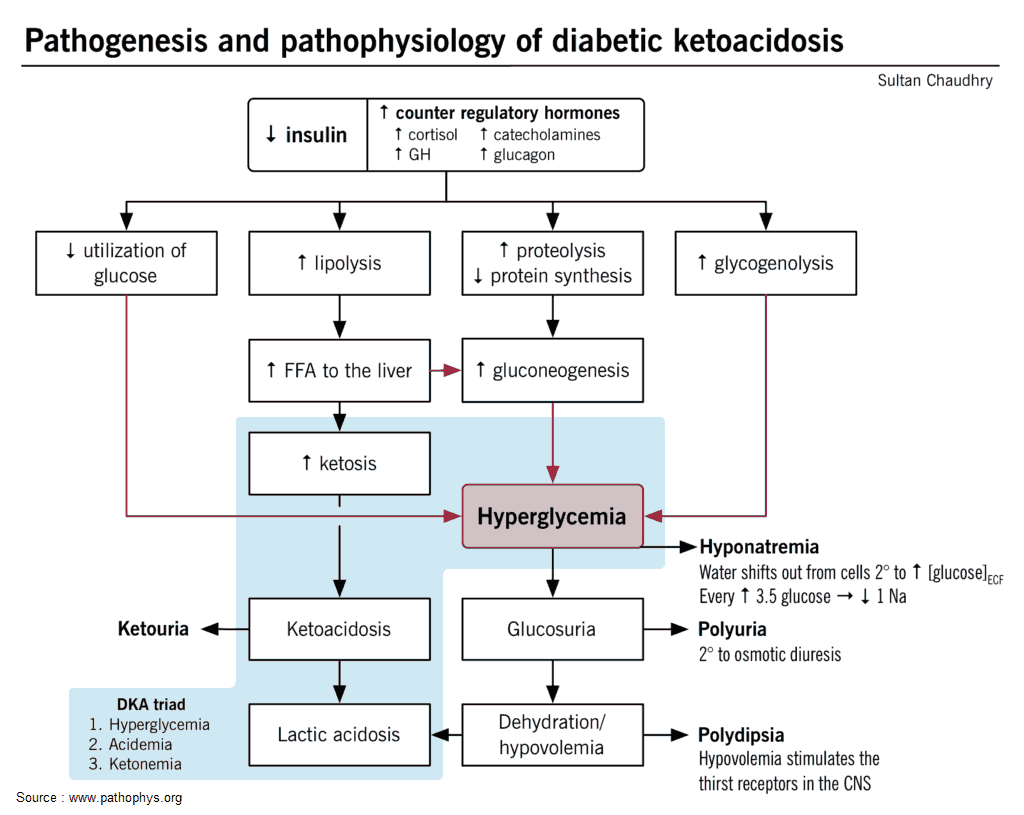 manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar hhs pathogenesis emergencies flowchart metabolic diabetes pathophys hyponatremia insulin acidosis
manualofmedicine.comketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology hyperglycemia hyperglycemic hyperosmolar hhs pathogenesis emergencies flowchart metabolic diabetes pathophys hyponatremia insulin acidosis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – Why Should It Matter To Me? | Nipro
 www.nipro-group.comketoacidosis dka diabetes nipro matter knowledge studying icu
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) | Type 1 Diabetes: Love Hailey | Diabetic
 www.pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes pathophysiology causes step1 medbullets endocrine insulin nursing deficiency glucose
www.pinterest.comketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes pathophysiology causes step1 medbullets endocrine insulin nursing deficiency glucose
Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) – why should it matter to me?. Ketoacidosis diabetic dka pathophysiology calgary nursing guide physiology pathology treatment medical concept map ucalgary calgaryguide ca hhs sheet complications bacterial. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka)